Abstract
Background: Waldenström macroglobulinemia (WM) is a rare indolent lymphoma accompanied by the secretion of clonal IgM. While chemo-immunotherapy (CIT) is still a widely adopted approach in treatment-naïve (TN) patients (pts), Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibition has become the new standard of care, especially in pts with relapsed/refractory (RR) disease. Zanubrutinib (ZAN, BGB-3111) is a second-generation BTK inhibitor with high specificity for BTK and reduced off-target inhibition of structurally related kinases. ZAN has recently been approved by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of WM in any line of therapy. This was based on a phase 2 study (Trotman et al, Blood 2020) and a randomized phase 3 study demonstrating non-inferiority to ibrutinib and an improved safety profile (Tam et al, Blood 2020). Between November 2020 and January 2022, an expanded access program of ZAN opened in Israel for the treatment of patients with RR-WM or those ineligible for CIT or ibrutinib in first line. We herein aim to provide real-world data on ZAN in pts with WM in Israel.
Methods: This is a multi-center retrospective study of patients with WM who were treated with ZAN within an expanded access program in Israel. Demographic and clinical data were collected from electronic files and coded according to center. ZAN dose, safety, and efficacy measures were recorded. Adverse events (AEs) of interest were specifically investigated. The response was evaluated by investigator-assessment according to the 6th International Workshop on WM (Br J Haematol. 2013). The program was closed by the sponsor for new accrual in January 2022. Active patients gradually transitioned to commercial ZAN once it was reimbursed by the Israeli Health Ministry. The study was approved by local IRB of each participating center.
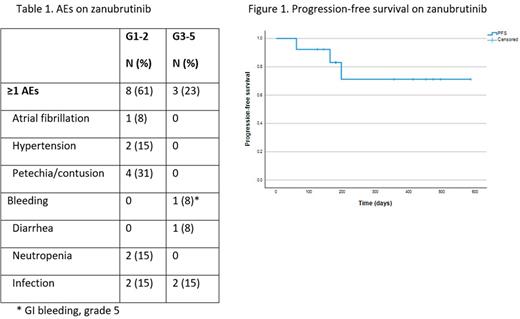
Results: Thirteen pts (12 RR; 1 TN) were enrolled from December 2020 to January 2022 across 8 medical centers in Israel. The median age at ZAN initiation was 71 years (range, 50-85); 6 were males; 12 were Jewish with a representative Ashkenazi-Sepharadi ratio and 1 Arab pt. RR pts had a median of 1 (range, 1-4) prior lines of therapy: mostly with rituximab-cyclophosphamide-dexamethasone (RCd)-like regimens (n=8), bendamustine-rituximab (n=7), and ibrutinib (n=4). One pt underwent an autologous stem cell transplantation. Other than progressive disease after CIT, the most common consideration for choosing ZAN were pts' age and/or comorbidities (n=5), as well as ibrutinib toxicity. In one representative case ibrutinib was associated with complete atrioventricular block; the patient was started on ZAN after AICD implantation. ZAN dose was 160 mg bid (n=8) or 320 mg once daily (n=1), yet 4 pts were given a reduced dose (160 mg per day) due to frailty. The median time on ZAN was 6.4 months (range 2-19.2). Of 12 evaluable pts, the overall response rate (ORR) was 83% with 3 (25%) minor responses, 6 (50%) partial responses, and 1 case of very good partial response (VGPR). Two pts had stable disease (SD). The median time to best response was 120 days. With a median follow up of 196 days (range, 61-585), 9 patients are still on therapy, 2 pts eventually progressed, 1 while on ZAN and 1 after ZAN was stopped due to an AE. The median PFS and OS were not reached (Figure 1). Eight (61%) pts had AEs of any grade, and 3 (23%) had grade 3-4 AEs. One patient died from GI bleeding 2 months after ZAN initiation. AEs of interest are depicted in Table 1. Three pts stopped ZAN due to the following AEs: GI bleeding, congestive heart failure, and extreme fatigue (one each).
Conclusion: The results of this real-world expanded access program are consistent with previously published data from trials with ZAN in WM. There were no new safety signals in this elderly frail cohort.
Disclosures
Itchaki:AstraZeneca: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy; Abbvie: Consultancy. Benjamini:AbbVie,Janssen,Astrazeneca: Consultancy. Raanani:Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Janssen: Speakers Bureau; BMS: Consultancy; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal